Because Congress sought out the power to regulate commerce. We propose that Republicans should do the.

Revisiting And Confronting The Federal Judiciary Capacity Crisis Charting A Path For Federal Judiciary Reform California Law Review
The federal government derives its authority to create law from Article I 8 which discusses federal Congresss exclusive or delegated powersThese include the power to regulate currency and coin establish a post office promote science and art by regulating the rights to.

Why did congress create an expanded federal court system. Congress created the first inferior courts of the federal judiciary in the Judiciary Act of 1789 but has expanded or dismantled parts of the federal court system at various points in. Federal courts created by Congress to exercise the judicial power of US. Population growth and geographical expansion required expanding the federal court system from the constitutional requirement of a Supreme Court in Washington to a system that could manage and administer justice throughout the growing country.
Jurisdiction of the Inferior Federal Courts. Because Congress had no power to pass laws c. This part of Article I Section 8 allows Congress to regulate commerce with foreign nations and among the.
The law in question was the federal Gun-Free School Zones Act. Also named the regular courts or article III courts. The first notable reversal from this expansive period came with the Courts 1995 decision in United States vLopez 16 in which for the first time since the 1930s the Court invalidated a federal law as exceeding Congresss Commerce Clause power.
Created by congress to hear cases arising out of some of the expressed powers given to congress in article I. In 1978 President Jimmy Carter and a Democratic-led Congress passed a judgeship bill that increased the size of the lower federal courts by 33 percent. Shapiro Hart Wechslers The Federal Courts and the Federal System.
The Scope of Federal Law. The Judiciary Act of 1789 established the federal court system separate from individual state courts. Supreme Court changed size seven times in its first 80 years from as few as five justices to as many as 10.
In 1801 Federalist party members in Congress sought to expand federal jurisdiction over the states by reorganizing the court system. Congress expanded the federal court system because the Constitution only established a Supreme Court and left it to Congress to create other. Because the Constitution only established the Supreme Court The nomination of candidates for President is an example of the influence of which group or entity in the interpretation of the Constitution.
Why did Congress create an expanded federal court system. The governments power to regulate comes from the US Constitution. Why did congress created federal an expanded federal court system.
99-16 99th Cong 1st sess. The most broad-ranging power of the federal government has become the Commerce Clause. Article Three of the US Constitution stated.
Because the Constitution establish only the Supreme Court d. It was one of the first acts of the First Congress. FOOTNOTES 1 To prevent an excess of citations to secondary authority we in this paper cite mainly to two basic authorities.
See full answer below. Izvoru47 and 11 more users found this answer helpful. Narrowing the scope of Congresss Commerce Clause power.
Because the Constitution established only the executive department b. Constitution of the United States of America -- Analysis and Interpretation S. The judicial Power of the United States shall be vested in one supreme Court and in such inferior Courts as the Congress may from time to time ordain and establish The first actions of the newly created Congress were to pass the Judiciary Act of 1789 that made provisions for the Supreme Court.
The congress created an expanded federal court system because the Constitution established the Supreme Court only. The Framers as we have seen1232 divided with regard to the necessity of courts inferior to the Supreme Court simply authorized Congress to create such courts in which then judicial power shall be vested and to which nine classes of cases and controversies shall extend1233 While Justice Story deemed it imperative of Congress to. Congress passed the Judiciary Act of 1801 creating new.
Why the Supreme Court ended up with nine justicesand how that could change. Article III did not cover how the court system would be developed so the First Congress created the Judiciary Act of 1789 to establish the federal Judiciary. Please mark as best answer.
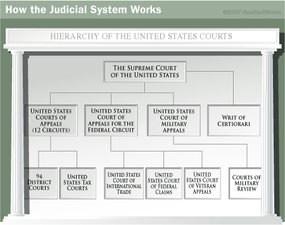
How The Judicial System Works Howstuffworks
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/21769394/869457204.jpg.jpg)
The Democratic Platform Calls For A Bold Remaking Of The Federal Judiciary It S Not Nearly Enough

Federalism State Sovereignty And The Constitution Basis And Limits Of Congressional Power Everycrsreport Com

Revisiting And Confronting The Federal Judiciary Capacity Crisis Charting A Path For Federal Judiciary Reform California Law Review

Why The U S Supreme Court Has Nine Justices

Revisiting And Confronting The Federal Judiciary Capacity Crisis Charting A Path For Federal Judiciary Reform California Law Review

How The U S Constitution Has Changed And Expanded Since 1787 History

Article I Section 8 Federalism And The Overall Scope Of Federal Power National Constitution Center

Revisiting And Confronting The Federal Judiciary Capacity Crisis Charting A Path For Federal Judiciary Reform California Law Review

Revisiting And Confronting The Federal Judiciary Capacity Crisis Charting A Path For Federal Judiciary Reform California Law Review

The Institutional Design Of Congress American Government

Revisiting And Confronting The Federal Judiciary Capacity Crisis Charting A Path For Federal Judiciary Reform California Law Review

The Evarts Act Creating The Modern Appellate Courts United States Courts

Revisiting And Confronting The Federal Judiciary Capacity Crisis Charting A Path For Federal Judiciary Reform California Law Review

The Federal Court System American Government

Three Branches Of Government History

Revisiting And Confronting The Federal Judiciary Capacity Crisis Charting A Path For Federal Judiciary Reform California Law Review